Spinal cord DWI
Diffusion imaging of the spinal cord
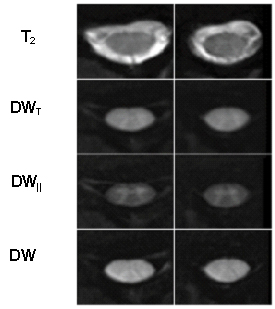
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) and diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) are of significant clinical interest as means of non-invasively providing information about structural integrity of and alteration to neural tissue. Investigations of diffusion characteristics in the spinal cord reveal new clinical insights into pathologies such as inflammatory demyelination, spinal cord infarction, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Wallerian degeneration, compressive myelopathy, spinal cord mass lesions and spinal cord trauma. Spinal cord DWI/DTI may be relevant both for early diagnosis, predicting outcome and for monitoring treatment effectiveness and recovery.
This project focuses on the improvement of hardware and acquisition technique for spinal DW imaging, which is complicated by physiological motion (particularly CSF pulsation), strong susceptibility gradients in the area around the spinal column and the inherently low signal-to-noise ratio of DW images.
References
- Wilm BJ, Gamper U, Henning A, Pruessmann KP, Kollias SS, Boesiger P. Diffusion-weighted imaging of the entire spinal cord. NMR Biomed 22(2), 174-181, 2009.
- Wilm BJ, Svensson J, Henning A , Pruessmann KP, Boesiger P, and Kollias SS. Reduced field-of-view MRI using outer volume suppression for spinal cord diffusion imaging. Magn Reson Med 57(3), 625-630, 2007.
Contact
No database information available